Overview, Aim, and Usages of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM)
This article will help you to understand the overview, aim, and usages of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM).
Overview
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring is the application of pharmacology, pharmacokinetic consultation, pathology and clinical medicine in the interpretation of measured drug concentration in body fluid.
OR
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring is a branch of clinical chemistry and clinical pharmacology that specializes in the measurement of medication concentrations in blood.
OR
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring refers to the measurement of drug concentration in a biological fluid with the purpose of optimizing a patient’s drug therapy.
Aim of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
The aim of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring is optimizing drug therapy by knowing the measured concentration and therapeutic effect and using this information is the case of the patient.
It’s used for measuring the drug concentration in body fluid including:
- Suspect toxicity due to drug metabolite.
- A sub-therapeutic response to drug therapy.
- Assessment of drug therapy where the patient is clinically unstable.
- Assessment of potential drug interaction.
- Evaluation of patient compliance.
Usages of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Mostly Therapeutic Drug Monitoring used in these two situations-
- For minimizing the risk of serious drug toxicity and assessment of the appropriateness of dosing for the drug used as prophylactic therapy.
- To identify the drug on substance, this may be contributing to the presentation of the medical emergency.
Some common usages of TDM
- To avoid drug toxicity and maintain the concentration of drug within a therapeutic range.
- To assist dose adjustment in various disease states where individual variation in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion (ADME) may be important.
- To minimize the time period needed for dosage adjustment (depending n half-life off drug).
- To identify the poison and asses the severity of poisoning on an emergency basis in a poisoned patient.
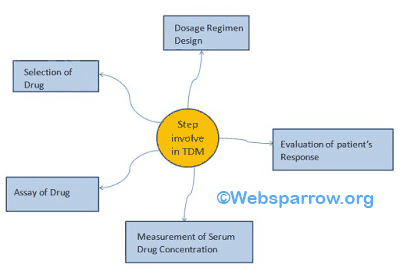
Steps involved in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
These following steps involved in TDM.
1. Selection of Drug
- Drug-selected on the basis of therapeutic consideration, therapeutic equivalency or cost and pharmacokinetic consideration.
- Patient-specific information is also considered like- medical history, allergies, drug sensitivity, etc.
2. Dosage Regimen Design
Its affected by numbers of factors:
- Pharmacokinetic of the drug.
- Physiology of the patient.
- Pathophysiologic condition.
- Personal lifestyle factor.
- Drug dosage form.
- Patient compliance.
3. Evaluation of patient’s Response
If the patient is not responding to the drug regimen, dosage regimen should be reviewed for adequacy, accuracy and patient compliance.
4. Measurement of Serum Drug Concentration
The blood sampling is done in the case when a patient is not responding as expected. Blood sampling time is taken during the post distributive phase for loading and maintenance doses. The blood sample is taken once steady state drug concentration has been achieved.
5. Assay for Drug
Assay of the drug is completed with the help of HPLC, Gas Chromatography, Spectrophotometer, Fluorometry and Immunoassay, and radioisotope methods.
Note: These above methods depend upon the following properties of the drug:
- Cost off assay
- Available instruments
- Amount and nature of biological specimen (serum, urine)
- Concentration for measurement
- Physiochemical characteristic of drug
- Concentration and measurement
References
Similar Posts
- Definition, Secretion, Regulation of Release, Function and Drawback of Growth Hormone(GH) in Pharmacy
- Importance and Methods of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
- Introduction, Classification and Mechanism of Action of Emetic and Antiemetic drug in Pharmacy
- Introduction + Classification + Pharmacological Action + Regulation of Release and Drawback of Glucocorticoids Hormone
- Introduction and Type of Autacoids in Pharmacy
- Source, Mode of Action and Pharmacological Action of Cardiac Glycoside
- Introduction and Uses of Diastase Enzyme
- Introduction, Pharmacological Action/Function, Regulation of release and Drawback of Progesterone in Pharmacy
- Definition, Functions and Types of Enzymes
- Introduction, Type, Advantage and Disadvantage of Hard Gelatin Capsule and Soft Gelatin Capsule in Pharmacy