Overview and Architecture of Oracle Database Server
This page will walk through overview and architecture of Oracle Database Server. An Oracle Database consists of at least one database instance and one database. Learn more about Oracle Database editions and features.
Oracle Database Server
An Oracle Database Server consists of an Oracle database and database instance. A database is a set of files that store data and a database instance is a set of memory structures (which manages database files) and consists of background processes.
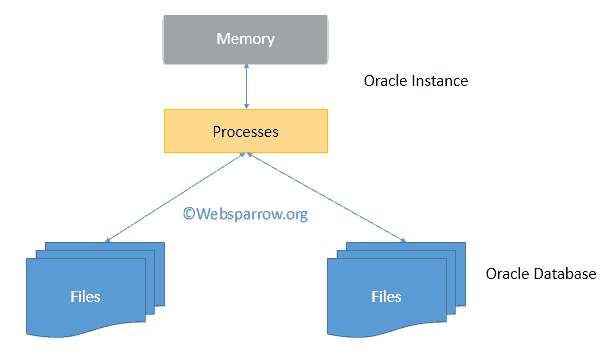
Note: Database can be shared between multiple database instances.
Oracle Database Server Architecture
There is two architecture in Oracle:
1- Dedicated Server Architecture
In Dedicated Server architecture if there are 100 users want to connect with the database server then each 100 user processes would be allocating 100 server processes and each server processes use the system resources including the CPU cycle and memory.
In a heavily loaded system, a Dedicated Server architecture can negatively affect the system’s scalability due to the high demand for server resources. In that situation, there are two options we have:
- Increase the system resource by adding memory and
- Additional CPU capability.
2- Shared Server Architecture
In a Shared Server process architecture, certain types of database work cannot be performed:
- Database administration
- Backup and recovery process
- Batch processing and bulk load operation
- Data warehouse operation